Contents of this blog:
Background
Definition
History
Importance
Handles large amounts of data Jobs created/ replaced
Types & Subfields of AI
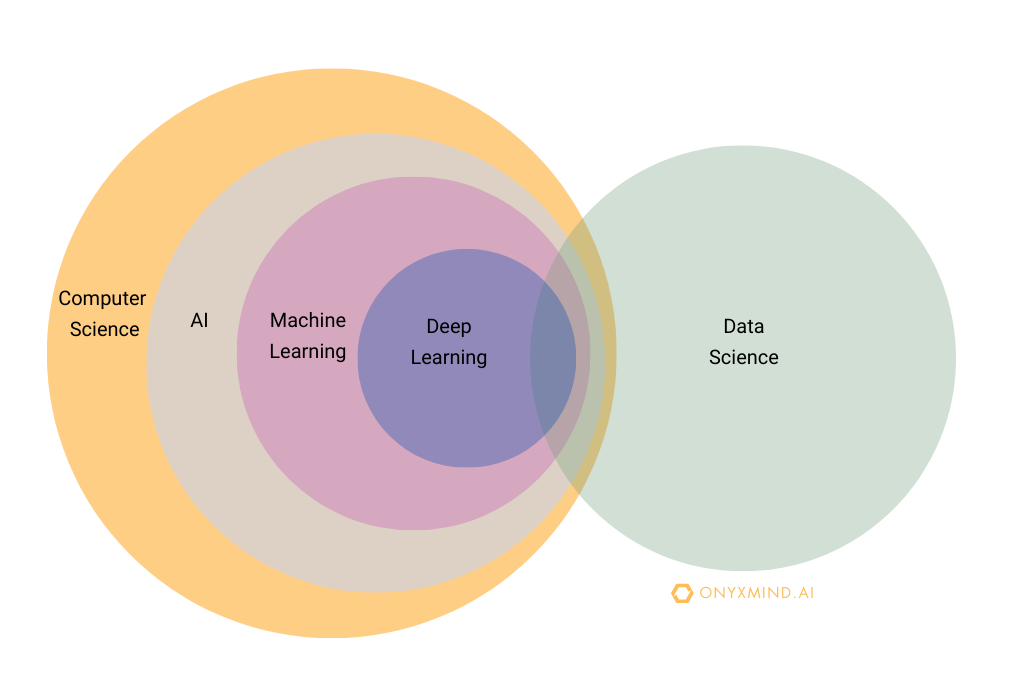
Subfields: Machine Learning, Deep Learning and Data Science.
Types of AI
Examples
Examples of everyday AI in your home
Background
AI stands for Artificial Intelligence. It is a field which uses algorithms and techniques to perform a task that mimics human intelligence. There are different types of AI, and each serves a different purpose, depending on what the task is. For example AI can be used to solve problems e.g. predictions, automation, recommendations, decisions or virtual environments. AI is built using large amounts of data to create a trained learning model. It is then coded using a programming language such as Python, C++, Rust and many more. The more data inputted in the model, the better the output. For example, the more a viewer rates their favourite Netflix shows the better Netflix can provide tailored future recommendations.
In the mid-20th century, Alan Turing, a famous british mathemetician and computer scientist published a seminal paper called “Computer Machinery and Intelligence”. This paper was the first to speak about Artificial Intelligence. Turing set out to answer the question “Can machines think?”. The conclusion was, machines cannot think intelligently like humans but can achieve similar through advancing machines. Today, when a complex AI model is built it is usually checked using the ‘Turing Test’. The Turing Test determines whether a machine can pose as a human being, undetected. Till today, there have been close contenders who have said to have passed the Turing Test. For example, Eugene Goostman, a chatbot which imitated a 13-year-old Ukranian boy is said to have passed the test as it won 33% of the judges vote.
Importance
Artificial Intelligence can outperform human tasks using large amounts of data. It is important for businesses to use AI to handle complex processes, data, reduce human errors or even make better future predictions. Humans are limited in performance, for example we cannot work 24/7 nor can we guarantee 0% error rates. We also tend to be biased in our decision making which are controlled by our cognitive biases. Using AI can reduce the risk of these. If AI can replace repetitive, dangerous tasks this inturn will allow a human workforce to better focus on other areas of the business which requires creativity or empathy. For example, building better client relationships or expanding the business.
AI has multiple subfields, which you would hear of everyday. The main subfields of AI are machine learning, deep learning and data science. To take it one step further, AI is part of an umbrella term: Compter Science. There are different types of AI which helps us understand what the aim of the task is. This is split into : Type 1 and Type 2.
Subfields of Machine Learning
Type 1
Narrow/ Weak AI AI is designed to perform a single task. E.g. Tracking weather updates, play chess, analyse raw data, image recognition, chatbots, predictive text, Siri. No ability to think.
General AI is currently a conceptual construct, but if achieved, machine intelligence would achieve full human cognitive abilities (common sense).
Strong AI focuses on reasoning & learning and thinking beyond human intelligence.
Type 2
Reactive Machines (ML) models with no memory and is task specific. Responds to identical situations in the same way. E.g. Recommendations based on watch/ purchase history
Limited Memory AI which stores previous data and predictions to make improved future predictions. E.g. self-driving car use sensors to identify civilians crossing the road
Theory of Mind is still under R&D, this is where a computer will understand human thoughts, emotions and beliefs. Can involve building a neural network, meta-learning to observe behaviours to integrate rich predictive analytics.
Self Awareness Machines are aware of human emotions as well as their own. Built by the machine analysing its own processes, decision-making algorithms and input.
Examples of everday AI
We use AI in our everyday lives, in our homes, our car and even our workplace:
Your Home:
- Netflix
The thumbnails which we click on are carefully generated by AI in order prompt more user click using frames from your favourite tv shows/ movies. This is done using Aesthetic Visual Analysis (AVA) which creates the thumbnail according to the genres and films you watch per region. This is why the thumbnails in your home may be different to your friend’s home. Firstly, each frame is annotated to indicate key variables within the content, for example saliency, brightness/ contrast, nudity probability or even skin tone. These labels create metadata for each frame and then grouped according to visualisation, composition & characteristics. Additionally, Netflix also uses another Machine Learning algorithm called, Contextual bandits where your thumbnail changes in real time.
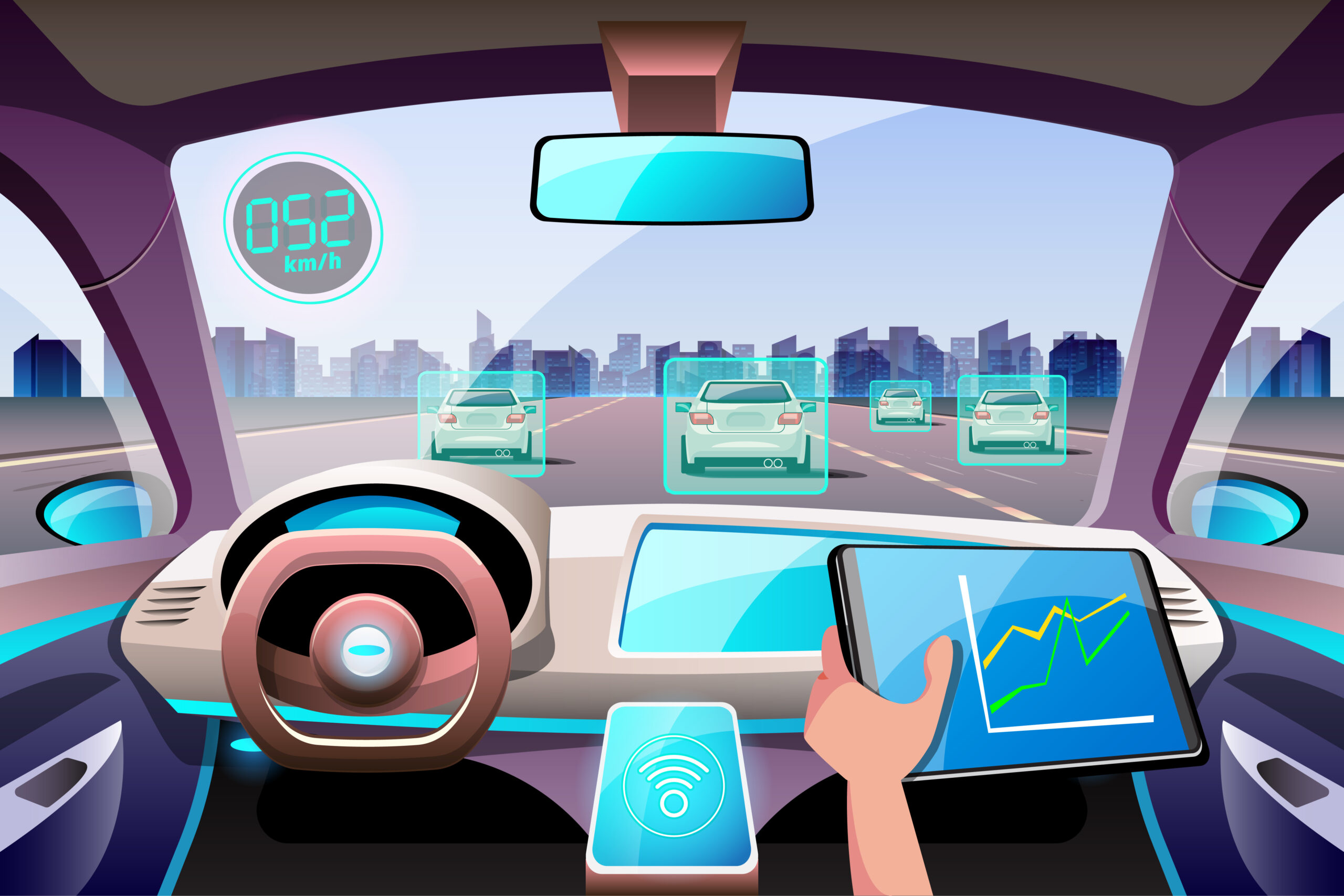
Your Car:
- Camera Detection
A vehicle operating autonomously will use sensors such as Light Detection and Ranging (LIDAR), cameras and ultrasonic sensors.This dataset is then used in Deep Learning, a type of AI, to create a trained model to aid in collision detection, cruise control and brake assist. For example LIDAR is a scanner to measure the distance of nearby objects and produces a 3D point cloud using the images. This how the computer sees the real world.
Image credit: source